Property Transfer in India: Step-by-Step Process
4.2K
The blog explains the legal process of property transfer in India, covering types of deeds, required documents, and charges like stamp duty. It outlines a clear six-step procedure: due diligence, agreement to sell, sale deed execution, stamp duty payment and registration, possession handover, and mutation of records for ownership update.
Contents
- Introduction to Property Transfer
- What is a Transfer of Property?
- Different Types of Property Transfer Options Available
- Sale Deed
- Transfer Deed
- Gift Deed
- Relinquishment/Release Deed
- Partition Deed
- Will Deed
- Documents Required for Transfer of Property
- Charges Applicable for Property Name Transfer
- Step-By-Step Process To Transfer Property in India
- Step 1: Due Diligence
- Step 2: Agreement to Sell
- Step 3: Sale Deed Execution
- Step 4: Payment of Stamp Duty and Registration
- Step 5: Handover and Possession
- Step 6: Mutation and Update of Records
- The Final Word
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I complete the property transfer process without a lawyer?
- How is stamp duty calculated, and what are the consequences of non-payment or underpayment?
- What documents are required for property ownership transfer in India?
- What is stamp duty and how is it calculated during property transfer?
Introduction to Property Transfer
There are different ways to make the transfer of property ownership in India. You can sell it, gift it, or relinquish ownership through specific deeds, depending on the situation. This blog provides a step-by-step guide on how to complete the property transfer process in India. It also answers other relevant questions you might have about the topic.
What is a Transfer of Property?
A transfer of property means transferring the ownership of a property from one person to another. In India, the Transfer of Property Act 1882 is the law that governs how to legally transfer property ownership. This law defines a property transfer as one living person giving their property rights to another person or multiple people, either immediately or in the future. The Act outlines the requirements, rights, and responsibilities involved in properly transferring a property from one owner to the next.
Different Types of Property Transfer Options Available
There are different ways to complete the name transfer of property ownership in India through various legal deeds:
Sale Deed
This is the most common way in the process of sale of property. The sale deed legally transfers the property's ownership to the new buyer after completing the sale.
Transfer Deed
This transfers a property's ownership rights from one owner to the next. Lenders can use it to transfer their rights in a property to someone else.
Gift Deed
A gift deed allows someone to transfer their property ownership to another person as a gift, without any payment. Used for gifting houses, jewelry, shares, etc.
Relinquishment/Release Deed
If a property has multiple owners, this deed allows one owner to transfer their ownership share to the other co-owners. Useful when an owner dies without a will.
Partition Deed
They are used to legally divide a jointly-owned property among the co-owners during the distribution of ownership.
Will Deed
This deed states how a person's assets/property should be distributed among their heirs after their death.
Documents Required for Transfer of Property
Here are the documents required for property transfer:
- Aadhaar card of seller and buyer
- Passport photos of seller and buyer
- Original copy of previous sale deed
- No Objection Certificate for Land Ceiling Act
- Latest property registration document
- A recent copy of the municipal tax bill
- Construction/building completion certificate
- Original agreement between builder and first buyer
Charges Applicable for Property Name Transfer
When selling or renting a property in India, you have to pay stamp duty on the legal agreements. In Maharashtra, this stamp duty is usually 4-7% of the property's value mentioned in the document. However, the exact stamp duty rates differ from one state to another.
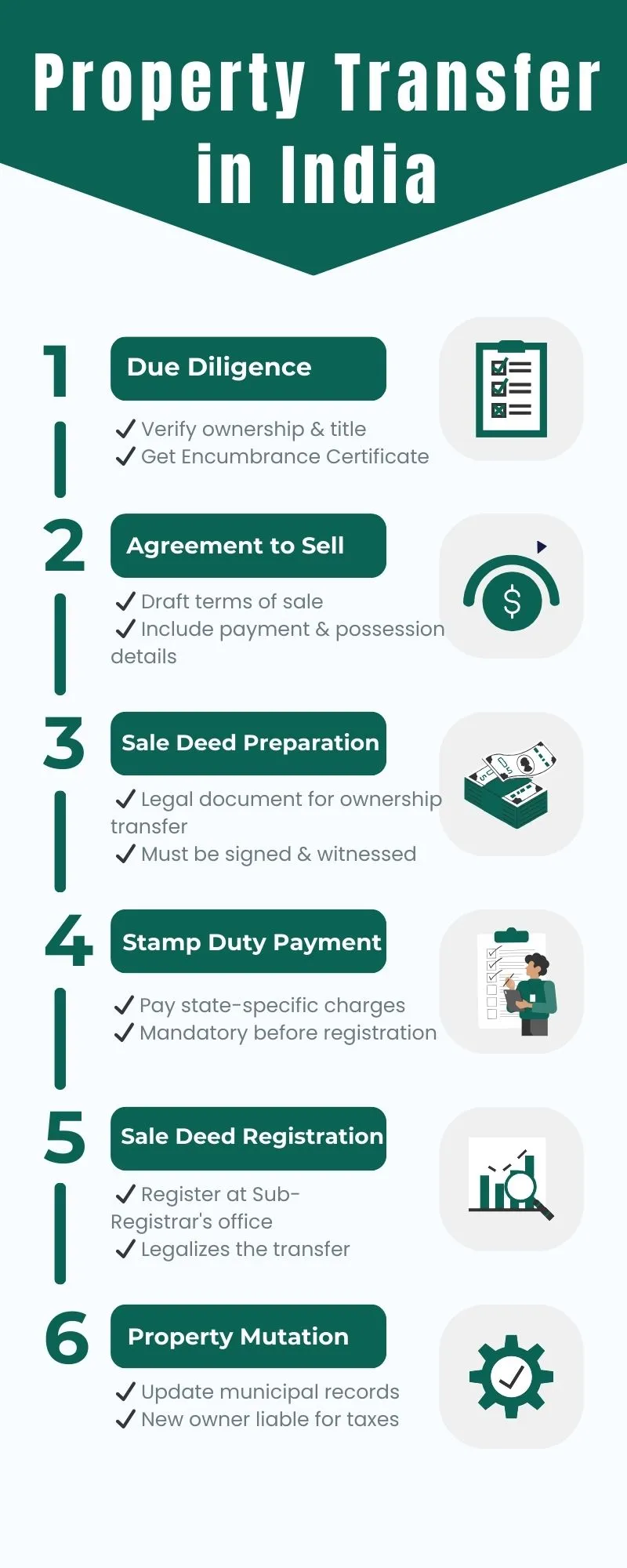
Step-By-Step Process To Transfer Property in India
Step 1: Due Diligence
Before initiating a property transfer, conducting thorough due diligence is essential. This includes verifying the property's ownership, title history, any encumbrances, and the legality of the construction. It is advisable to engage a lawyer to scrutinise the relevant documents, such as the sale deed, title deed, encumbrance certificate, building approvals, and property tax receipts.
Step 2: Agreement to Sell
Once the due diligence is completed and both parties are satisfied, an agreement to sell is executed. This agreement outlines the terms and conditions of the sale, including the sale consideration, payment schedule, possession date, and any other relevant clauses. It is important to ensure that the agreement is legally binding and signed by both parties.
Step 3: Sale Deed Execution
After the agreement to sell, the next step is the execution of the sale deed. The sale deed is a legal document that enables the transfer of name in property records from the seller to the buyer. It includes details such as the property description, sale consideration, rights and obligations of both parties, and other necessary clauses.
Step 4: Payment of Stamp Duty and Registration
Stamp duty is a state-specific tax imposed on property transfers. The buyer is responsible for paying the stamp duty based on the property's market value or the sale consideration, whichever is higher. It is crucial to calculate the applicable stamp duty and make the payment at the designated bank.
Step 5: Handover and Possession
Once the sale deed is registered and all financial obligations are fulfilled, the seller hands over the possession of the property to the buyer as per the agreed-upon possession date. A joint inspection may be conducted to ensure that the property is delivered in the agreed condition.
Step 6: Mutation and Update of Records
After taking possession, the buyer should initiate the process of mutation. Mutation involves updating the property records with the buyer's name as the new owner. This process is typically carried out at the local municipal corporation or panchayat office. The buyer should submit the necessary documents, updated property tax receipts, and identity proofs, to complete the mutation process.
The Final Word
Property transfer in India follows a systematic step-by-step process that encompasses due diligence, agreement to sell, execution of the sale deed, payment of stamp duty and registration, possession handover, and mutation of records. Adhering to the legal requirements and ensuring proper documentation is crucial for a smooth and legally valid transfer of property ownership.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I complete the property transfer process without a lawyer?
Ans. While it is possible to navigate the process without a lawyer, it is advisable to engage a legal professional to ensure compliance with the legal requirements and protect your interests.
How is stamp duty calculated, and what are the consequences of non-payment or underpayment?
Ans. Each state in India has its own stamp duty rates, which may vary depending on factors such as the property type, location, and gender of the buyer or seller.
What documents are required for property ownership transfer in India?
Ans. The main documents required are - the original sale deed, property registration papers, latest tax receipts, approved building plans, No Objection Certificates, and ID proofs of the seller and buyer.
What is stamp duty and how is it calculated during property transfer?
Ans. Stamp duty is a tax paid when transferring a property. It is usually 4-7% of the property's market value or sale value, whichever is higher. The exact stamp duty rate differs in each state.


